Nuclear Medicine
Nuclear medicine is an advanced, specialised and reliable area in radiology, where radioactive materials known as radioisotopes, radiotracers or radiopharmaceuticals (technetium, thallium, gallium, xenon, iodine, fluorine, etc.) are used both in diagnostic and treatment procedures.
Aimed at curtailing the progression of cancers related to the thyroid gland, lymphomas, hematomas and various other tumours, nuclear medicine is often referred to as ‘radiology done inside out’, or ‘endoradiology’. This advanced medical speciality not only helps the nuclear medicine specialists and oncologists in understanding the detailed functioning of the organs, growth of cancer cells, tissues, structure, but also provides them with the necessary information to decide upon the further course of treatment, even as tiny amounts of radioactive materials ‘taken up’ and emitted within the body lay down a detailed view.
Nuclear medicine, an integral part of diagnosing and treating medical conditions since the 1950s, is an eclectic mix of disciplines including mathematics, chemistry, physics, computer technology besides medicine. It has picked up pace in the last two decades owing to vast scientific advancements in the field of medicine, especially revolutionising cancer care.
How Does Nuclear Medicine Work?
Nuclear medicine is a vastly applied sophisticated medical technique across various specialities including heart, gastrointestinal, neurological, endocrine conditions and cancers for assessing, evaluating, diagnosing and treating these conditions. Small amounts of radioactive materials called radiotracers are injected into the body, which project images with a detailed view.
Another prominent branch of nuclear medicine is nuclear medicine therapy wherein radioactive iodine (I-131) is used for treating thyroid cancer, radioactive antibodies are injected for curtailing cancer of the lymphatic system or lymphoma, for alleviating painful metastases of tumours into the bones and also for stopping the progression of cancer cells in adrenal glands in adults and tumours of nerve tissues in children.
Radioimmunotherapy and brachytherapy are two other treatment procedures under nuclear medicine that are having promising results in treating various types of cancers.
Advantages
Well, advanced techniques in nuclear medicine came as a shot in the arm for treating even the toughest of cancers.
Diagnosis of Cancer:
One of the primary steps while suspecting cancer or tumour growth is to get an accurate diagnosis, and it can be achieved after running radiology tests and correlating the same with blood work. Nuclear medicine serves like an X-ray, however, while the latter passes x-rays through the body for getting images, the radiotracers in this advanced technique create pictures with the help of special cameras that read into the processes within the body.
In a majority of cases, radiotracers are injected into the body intravenously, but one may be asked to swallow it in the form of a pill or inhale it as a gas. These tracers accumulate, giving off gamma rays detecting the spots of intense activity, based on the metabolism and other chemical activity.
If the radiation collects in great amounts projecting ‘hot spots’, on the image, it is indicative of a tumour. However, cancer growth can also show up as a ‘cold spot’ with lesser cellular activity and still be a tumour.
1. PET/CT
PET – Positron Emission Tomography or Computed Tomography plays a vital role in detecting cancers, where radioactive tracer in small amounts gets injected into the body intravenously. In certain cases, the expert oncologist may ask for injecting a ‘dye’ or contrast material for procuring multiple three-dimensional images.
A combination of PET/CT is often the most recommended diagnostic tool as it not only helps in detecting the presence of cancer cells but also in finding if it had spread to other organs, evaluate the progress of treatment, cancer remission or if it recurred, besides the viability of tissues.
Treatment of Cancer:
There are various types of nuclear medicine treatments available in cancer care.
1. Radioactive Iodine Therapy:
The first line of treatment in thyroid cancer, radioactive iodine (RAI or I-131) is injected which gets collected into the thyroid gland for killing the thyroid cancer cells and also preventing it from spreading to other parts of the body, especially the lymph nodes.
The same therapy also comes in handy for treating hyperthyroidism.
2. Radioimmunotherapy:
This particular treatment is recommended for patients suffering from non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma but not responding to chemotherapy. A combination of radiation therapy and immunotherapy, monoclonal antibodies may be injected into the body which not only targets cancer cells but also kicks in the body’s immune system.
Studies are also on to find out if radioimmunotherapy can be applied in cases of prostate cancer, colorectal cancer, leukaemia, melanoma, brain glioma.
3. Brachytherapy:
A non-invasive or minimally invasive therapy includes delivering high doses of radioactive material into the body for killing cancer cells. Unlike conventional radiation therapy, it targets specific areas and has lesser side effects, as it uses external beams outside the body even while radiation gets induced into the cells.
Brachytherapy aids in treating various cancers including, breast, brain, cervical, endometrial, esophagus, bile duct, head and neck to name a few.
Nuclear Medicine at HCG
HCG has always been at the forefront of bringing in highly advanced diagnostic tools and treatment options for the benefit of its patients.
The nuclear medicine department at HCG is fully-fledged and houses some of the highly advanced diagnostic and therapeutic platforms to support effective treatment and management of a broad spectrum of cancers.
Following are the features of the nuclear medicine department at HCG:
- The department is equipped with two state-of-the-art SPECT CT Gamma Cameras.
- The department houses two high-end digital PET CT machines by Siemens Vision 600 to deliver high-resolution and superior quality diagnostic support.
- The centre has ten dedicated isotope therapy rooms to offer theranostic services; HCG houses the largest theranostics facility in India.
- Our nuclear medicine specialists have vast experience in administering I-131 therapies for the cancer of the thyroid gland, targeted isotope therapies, such as Lu177 PSMA, Lu177 dotatate.
- In association with the well-established interventional radiology department, our nuclear medicine department is also the first in the country to offer intra-arterial therapies using Lu177 Dotatate, Actinium Dotatate, Actinium FAPi, Actinium Dotatate therapies and I131 Lipiodol for hepatocellular cancers / hepatic metastases.
Firsts from HCG’s Nuclear Medicine Department
- HCG is the first centre in India to establish the medical cyclotron for the production of PET CT tracers as per CGMP norms. It is the only centre to produce 10 different types of PET tracers on a routine basis to solve complex clinical diagnostic challenges.
- HCG is the country’s first centre to offer Actinium (Alfa) therapies for advanced cancers of the prostate and neuroendocrine tumours
- HCG is the first centre in the country to offer FAPI scans on a routine daily basis.
- HCG is also the country’s first centre to offer Lu177/Actinium FAPi therapies for FAP positive advanced cancers.
- It is also the first centre in the country to obtain NABH MIS accreditation for imaging services using the PET CT platform.
Theranostics
HCG – the Specialist in Cancer Care has left no stone unturned to ensure that it delivers the highest quality diagnostic treatment support to its patients. Through constant research and innovation, we aim to help patients receive the right care, the first time.
The introduction of theranostics in cancer care for the first time in India is one of the upsides of our nuclear medicine department’s consistent research towards bettering cancer care.
The term ‘theranostics’ is derived from the phrases ‘therapeutics’ and ‘diagnostics’. Drugs and/or procedures are uniquely integrated to diagnose and treat medical disorders concurrently or sequentially in this growing branch of medicine. This is a classic example of evidence-based medicine in action.
The capacity to obtain a diagnosis and give therapy in one package is a game-changer for modern medicine. This also sits well with HCG’s aim to deliver patient-centric cancer care. Not only does this approach save time and money, but it also has the ability to avoid some of the negative outcomes that may occur when these strategies are used independently.
Case Study Demonstrating the Efficacy of Theranostics:
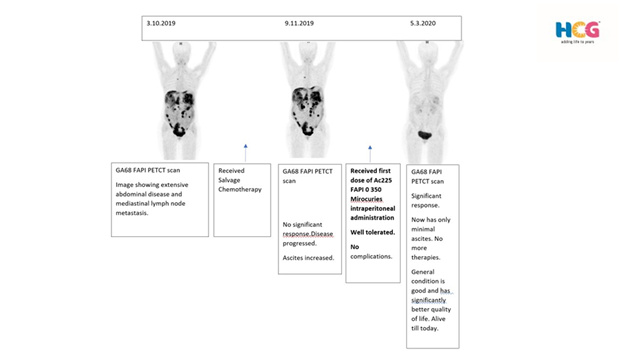
A 50-year-old woman presented herself with a carcinoma ovary. She had undergone all standard/established therapies to treat her disease. However, the disease progressed. All therapeutic options were exhausted. As a last resort, a Ga68 FAPi scan was performed, which revealed an advanced disease. This was followed by Ac225 FAPi therapy which showed an amazing response. Currently, many end-stage cancers are being treated similarly for patients who have no other promising treatment options.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. Will I be radioactive after a nuclear medicine scan?
The nuclear imaging agent injected into the body gets decayed naturally and flushed out of the system completely within 60 hours through urine or stool. Drinking lots of water helps in losing the radioactive agent at a faster pace.
2. Are nuclear medicine tests safe?
Yes. Nuclear medicine tests and treatment procedures are absolutely safe. A carefully picked up radioactive tracer and sparse doses of radioactive substances injected into the body provide accurate results. In other words, it is as safe as a diagnostic X-ray.
3. Does nuclear medicine have side effects?
Nuclear medicine doesn’t cause any particular side effects. Few allergic reactions, which are extremely mild, are reported rarely in certain patients. One shall not experience any adverse side effects post diagnostic or treatment procedures.
4. Are nuclear medicine scans painful?
Nuclear medicine scans are non-invasive procedures and are painless. One might experience a mild prick while getting injected with radioactive material and it won’t persist for more than 5 to 10 seconds.
5. Can pregnant women and breastfeeding mothers undergo nuclear medicine scans?
Nuclear scans are contraindicated in pregnant women.
The lactating mothers should stop feeding the baby for a day or two, as radioactive material can still pass on to the baby via breast milk.
6. How long does a nuclear medicine scan take?
It takes up to 30 to 60 minutes for a detailed nuclear medicine scan. In case of bone-related diagnosis, it can take up to 2 to 3 hours as the bones would require more time for the radioactive material to get absorbed. The scan will take about an hour.
7. How long will it take for me to receive my nuclear medicine scans?
It takes up to 30 to 60 minutes for a detailed nuclear medicine scan. In case of bone-related diagnosis, it can take up to 2 to 3 hours as the bones would require more time for the radioactive material to get absorbed. The scan will take about an hour.
The results will take up to 24 – 48 hours.
8. Is it ok to be around children after my nuclear scan?
Yes. You can be around pregnant women and children post the nuclear scan. However, avoid sleeping next to a pregnant woman or a child on the night of the scan and wait till the next morning for the radioactive substance to completely leave the body.
9. Is radioactive iodine therapy safe?
RAI or Radioactive Iodine Therapy is a completely safe, reliable treatment plan recommended in certain types of thyroid cancers.
10. Are there any long-term side effects associated with radioactive iodine therapy?
In certain patients, the long-term side effects associated with radioactive iodine therapy include infertility, fatigue, dry or watery eyes, swelling of the salivary glands, low blood count. These side effects will not last for long and the patient will be back to normal within a few weeks after completion of the treatment.
11. How long does it take for the radioactive iodine therapy to work?
It may take up to 1 to 3 months for the radioactive iodine therapy to work and the results may last for six months. However, few patients might require it for every three months, till thyroid cancer gets cured completely.